Our Location
Every component in our modern world, from the screws in your kitchen cabinets to the intricate parts inside a spaceship, shares one commonality: they are often produced using CNC machining. CNC, which means Computer Numerical Control, has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by enabling precise, three-dimensional cutting tasks to be executed from a single set of instructions. To truly appreciate the wonders of CNC machines, it is important to explore their origins and understand their evolution.
CNC machining has revolutionized the manufacturing of parts and components across various industries, including aerospace, electronics, military, and medical sectors. Exploring the history of CNC machining is not just about delving into an intriguing past; it also provides insight into a future where advancements in CNC technology may lead to even greater innovations.

Table of Contents
ToggleCNC machining is an advanced and complex manufacturing process that applies computerized systems to control machine tools. These tools, including mills, lathes, and grinders, perform precise and intricate cuts on raw materials to create finished parts. The advantage of CNC machining is its ability to produce highly accurate components that would be impossible to achieve using manual methods.
CNC machining relies on a computer program that controls the movements of the machine tool. Technicians input precise instructions, usually developed through CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The computer interprets these instructions and directs the machine to control the cutting tool’s speed, depth, and path. This automated process ensures greater consistency and repeatability in production while also reducing the likelihood of human error. 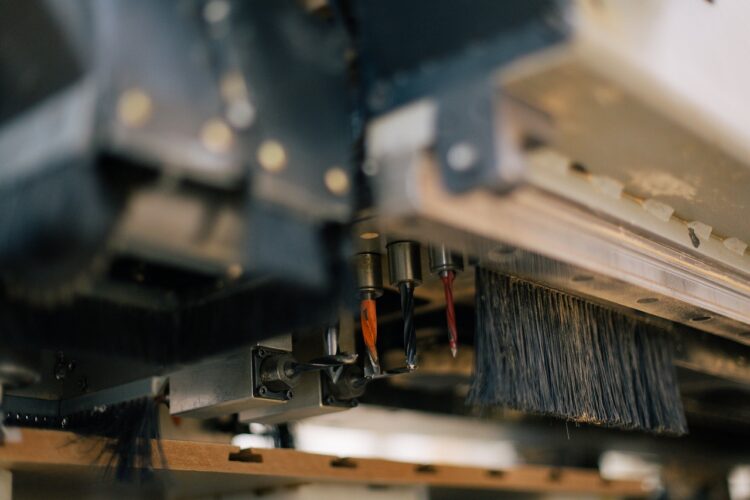
Many industries require tools produced through high-precision manufacturing processes. One of the most notable industries with this need is aviation. Given that they are responsible for human lives, their machinery mustn’t be made from low-quality or imprecise manufacturing methods. Therefore, they rely on the high precision capabilities of CNC machining. When you choose Rapid Direct, you benefit from an impressive tolerance standard of 0.0002 inches.
One significant advantage of CNC machining is its high level of accuracy. The programming codes and operator controls enable it to produce parts that match the specifications outlined in the CAD file precisely. As a result, you can be confident that when multiple parts need to fit together into a larger component, they will align seamlessly.
CNC machines can produce complex geometries that are difficult and time-consuming with manual methods.
The versatility and accuracy of CNC machining make it the preferred choice for components with complex shapes, undercuts, and intricate details, such as turbine blades or medical implants.
The origins of CNC can be dated back to the Industrial Revolution occured in the late 18th and early 19th century when steam-powered machines began to replace manual labor. As mass production methods were introduced, the demand for precision machinery grew, leading to the need for standardized and interchangeable parts.
The quest for precision led to the development of the milling machine, marking a significant milestone in the history of machining. This innovation represented a shift from manual labor to mechanized production. However, the question of who invented the milling machine is a topic of debate. Many credit American inventor Eli Whitney with creating the first milling machine, while others argue that it was skilled mechanic Roswell Lee who deserves this recognition.
The first semi-automated machine, known as the turret lathe, was developed in the mid-19th century. This invention marked an earthshaking advancement in the history of CNC lathe machines, laying the groundwork for fully automated machining. The turret lathe was capable of producing identical complex parts at high speeds, representing a substantial improvement in manufacturing efficiency.
Although the turret lathe was a significant development in the history of machining, it is important to note that it was not a CNC machine. These machines were mechanically automated, lacking the digital control that defines modern CNC machines.
With the growth of telecommunications in the 19th century, punched tape became a crucial component for early automation. The first numerical control (NC) machines used punched tape to provide instructions, marking a significant turning point in the history of computer numerical control (CNC).
As we explore the history of CNC technology, one figure stands out: John T. Parsons. Many consider Parsons to be the father of modern CNC. The concept of numerical control machining began to take shape when Parsons received a contract in 1949 to manufacture helicopter rotor blades.
Parsons collaborated with Frank Stulen to develop a system for producing blade templates using data points processed by a basic computer. These data points were transferred onto punched cards, which instructed the milling machine. This innovative approach is recognized as the first CNC machine, marking a significant milestone in the history of CNC milling machines.
The aircraft industry significantly contributed to the advancement of CNC machining by generating the demand and funding needed for the technology’s continued development. Recognizing the potential of Parsons’ invention, the Air Force provided financial support for additional research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
In 1952, MIT created the first true numerical control machine. This machine utilized a series of numbers punched onto a roll of tape to control its movements. This method was significantly more accurate and flexible than previous systems, laying the foundation for the development of modern CNC machines.
While the punched tape method was a significant breakthrough, it had limitations. The tapes were susceptible to wear and tear, leading to errors, and changing the machine’s commands necessitated creating a new tape.
In the 1960s, the introduction of computers marked the beginning of the CNC machining era. The shift from punched tape to digital programming was a crucial turning point in the history of CNC. This advancement allowed CNC machines to run a program multiple times, resulting in higher production rates and increased precision. Consequently, it ushered in a new era in the history of precision machining.
In the late 20th century, the emergence of computer technology revolutionized the CNC machining industry, enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and versatility of CNC machines. In the timeline of CNC history, the introduction of computers stands out as a significant milestone, as it enabled the digital storage of intricate designs and automatic error correction.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) were integrated into the CNC machining process, revolutionizing how components are designed and manufactured. This advancement in the history of CNC machinery marked the beginning of a new era in production, allowing designs to be tested and modified virtually before being sent to the manufacturing floor.
The combination of CAD and CAM in CNC machining optimized the manufacturing process. Designs could be created in CAD software and then translated into a language compatible with CNC machines using CAM software.
The integration of CAD and CAM in CNC machining has led to fewer errors, faster turnarounds, and lower costs, resulting in a more efficient and effective manufacturing process. This represents a significant advancement in the history of CNC machining.
5-Axis Machining
As we progress through the history of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, we come to the development of multi-axis machining. Multi-axis machines, such as the 5-axis CNC machine, can move in multiple directions simultaneously. This capability enables the creation of complicated parts with a high level of precision.
Multi-axis machining has significantly enhanced the capabilities of CNC machines, enabling manufacturers to create more intricate designs in a shorter time. This innovation marks a momentous advancement in the evolution of CNC machines.
Industrial machines, such as CNC machines, lathes, and milling machines, often require highly accurate components. CNC machining is utilized to create parts such as gears, shafts, and other precision components for industrial machinery.
The automotive industry heavily depends on CNC machining for many applications. CNC machines produce precise parts for engine components, suspension systems, gears, and custom accessories, ensuring high performance and durability in vehicles.
In aviation and space exploration, precision is crucial. This is where CNC machining plays a vital role. This technology is ideal for producing the intricate parts needed for airplanes, helicopters, satellites, and spacecraft. Parts such as landing gears, turbine blades, and engine parts demand extremely tight tolerances, and CNC machines can achieve that with ease.
CNC machining is extensively utilized in the electronics industry to produce components such as connectors, enclosures, and circuit boards. These parts must fit together precisely, requiring high precision to ensure proper functionality.
In the medical field, precision is essential. CNC machining is utilized to produce medical components such as surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics, where even the smallest error could lead to serious consequences.
CNC machining plays an enssential role in the energy sector, whether it involves oil and gas drilling equipment or components for wind turbines and solar panels. It is essential for manufacturing parts designed to withstand high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, such as turbine blades and valves.
The defense industry demands a range of high-performance parts, including weapons systems, vehicles, and aircraft. CNC machining is essential for manufacturing components that must adhere to strict standards of durability, reliability, and performance.
CNC machining is widely utilized in architecture and construction to produce detailed components and materials, such as custom doors, windows, and intricate woodwork. Whether for residential or commercial projects, CNC machining can create precision parts that fit seamlessly into building designs.
For inventors, product designers, and engineers, CNC machining is often the initial step in transforming a new idea from concept to reality. Whether it’s creating a prototype of a new product or manufacturing custom parts for a specific project, CNC machines can quickly and accurately bring those ideas to life.
Our journey through the history of CNC machining spans over a century, beginning with the first rudimentary automated machines of the Industrial Revolution and leading to today’s advanced multi-axis CNC machines. This progression illustrates how CNC machining has continually evolved and improved over time, fueled by technological advancements and the increasing demand for precision, speed, and versatility in manufacturing.
While the history of CNC machining is fascinating, the future of this technology is even more exciting. With ongoing advancements in computer technology, materials science, and automation, the possibilities for CNC machining are virtually limitless.

